The 7th Pay Commission (7th CPC) brought significant changes to the pay and pension structure of central government employees and pensioners. For retirees, the revised pension calculation under the 7th Pay Commission is crucial to understand, as it determines their monthly pension and arrears.
This guide explains the 7th Pay Commission revised pension calculation, the role of the pay matrix, and step-by-step examples to help civilian pensioners clearly understand how their pensions are determined.
What is the 7th Pay Commission?
The Government of India periodically sets up Pay Commissions to revise the salaries, allowances, and pensions of its employees. The Seventh Central Pay Commission (7th CPC) was implemented on 1st January 2016, affecting more than 47 lakh employees and 52 lakh pensioners.
One of its main goals was to rationalize the pension calculation process, ensuring fairness and simplicity while maintaining parity between past and current pensioners.
Also read: List of Central Pay Commissions in India: 1st to 8th CPC Salary & Pension Hikes!
Key Features of 7th CPC Pension Revision
- Applicable to all civilian pensioners retiring before 01-01-2016.
- Pensions are revised using two methods; the higher of the two is granted.
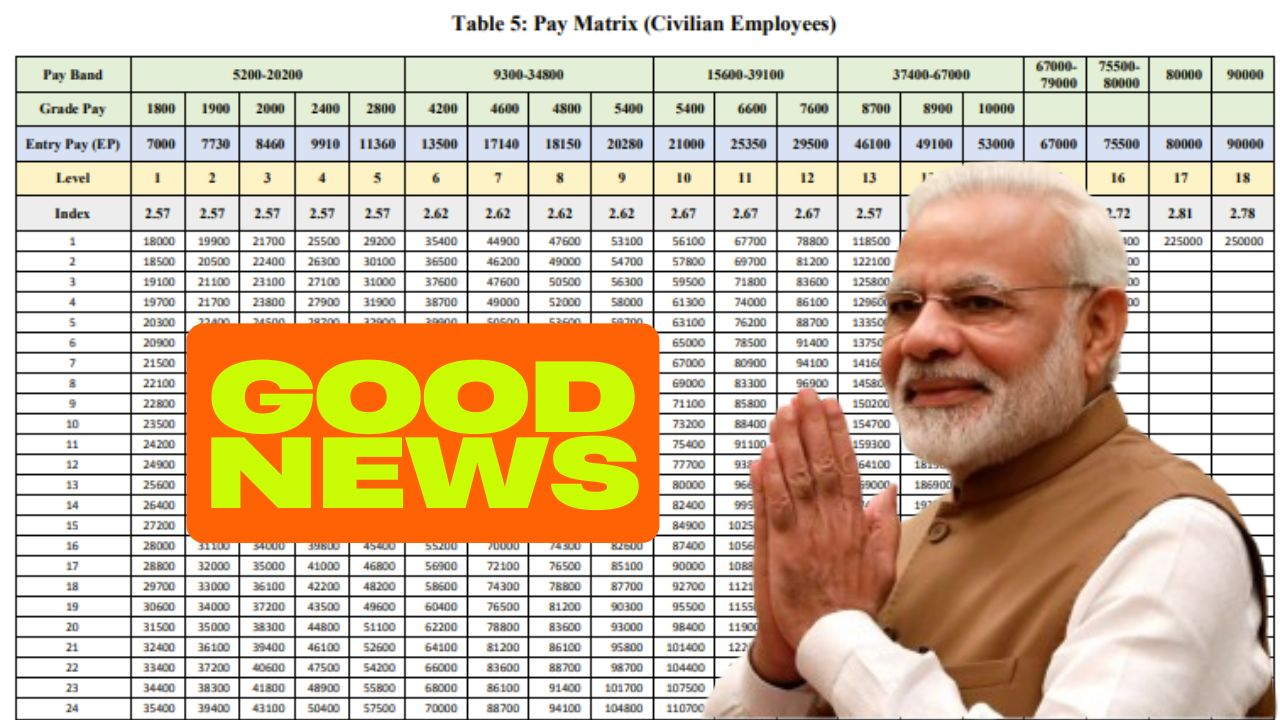
- Introduction of the Pay Matrix, which standardizes pay scales across grade levels.
- Fitment factor of 2.57 applied uniformly to existing pensions.
- Ensures protection of pensioners’ interests by allowing the higher value between two calculations.
Methods of Pension Calculation under 7th CPC
The 7th Pay Commission pension revision allows pensioners to choose the better of two options:
Method 1: Multiplication by Fitment Factor
- Pension fixed under the 6th Pay Commission is multiplied by 2.57.
- Formula:
Revised Pension = 2.57 × Pension fixed at 6th CPC - This provides an interim revised pension amount.
Method 2: Notional Pay in the Pay Matrix
This method is based on the last drawn pay and corresponding pay matrix level.
Steps:
- Find Pay Band and Grade Pay: Identify the pay band and grade pay corresponding to the last drawn salary.
- Locate in Pay Matrix: Using the pay matrix table, find the minimum basic pay at that level.
- Add Increments: For every increment earned before retirement, add 3% per increment to the basic pay.
- Calculate Notional Pay: The resulting figure after increments is the notional pay.
- 50% Pension Rule: Pension is fixed as 50% of notional pay.
Finally, the pensioner will receive whichever is higher between Method 1 and Method 2.
Example of Pension Calculation
Let’s understand with a practical example:
- Pension fixed as per 6th CPC = ₹10,000
Step 1: Interim Pension (Method 1)
= 2.57 × 10,000
= ₹25,700
Step 2: Notional Pay in Pay Matrix (Method 2)
- Last drawn pay falls under Pay Band 37400–67000 with Grade Pay 10,000.
- As per pay matrix, minimum basic = ₹1,44,200.
- Suppose the retiree had 5 increments at retirement.
Notional Pay = 1,44,200 × (1 + 3%)^5
= ₹1,67,200 (approx)
Revised Pension = 50% of 1,67,200
= ₹83,600
Step 3: Compare
- Method 1 = ₹25,700
- Method 2 = ₹83,600
Since Method 2 is higher, the final revised pension will be ₹83,600.
Initially, pensioners receive Method 1 (interim pension), followed by Method 2 with arrears paid later.
Understanding the Pay Matrix in Pension Calculation
The Pay Matrix introduced in the 7th CPC simplifies salary and pension determination. It merges the earlier pay bands and grade pay system into a single structured table.
- Each level corresponds to a post and grade pay.
- Vertical movement in the matrix shows increments (3% per year).
- Pensioners can simply move down rows to calculate their notional pay.
This ensures parity between past and current retirees. A person who retired earlier with the same rank and years of service should not be at a disadvantage compared to someone retiring after 2016.
Benefits of 7th CPC Revised Pension
- Fairness for all pensioners: Protects older pensioners from receiving lower pensions.
- Transparency: The pay matrix makes pension calculations simple and logical.
- Higher Take-home Pension: Many retirees benefit more under Method 2.
- Arrears Payment: Pensioners also receive arrears when their pensions are refixed.
- Parity Across Generations: Ensures equal pension for equal service, regardless of retirement date.
Challenges in Implementation
While the 7th CPC pension rules are beneficial, some challenges exist:
- Complexity in calculating notional pay for pensioners with multiple increments.
- Initial delays in disbursing revised pensions and arrears.
- Confusion among pensioners about which method is applied.
Despite these, the pension revision system remains one of the most beneficial changes introduced by the 7th Pay Commission.
Conclusion
The 7th Pay Commission revised pension calculation ensures fairness, transparency, and higher benefits for central government pensioners. By applying both fitment factor multiplication and notional pay in the pay matrix, the system guarantees that retirees receive the maximum possible pension. For many pensioners, the pay matrix-based calculation (Method 2) results in a significant increase compared to the interim pension. With arrears and parity benefits, the 7th Pay Commission pension structure has been a major step forward in improving the financial well-being of India’s retired government employees.
Also read: 7th Pay Commission Pay Matrix & Fitment Factor 2025: Complete Guide
FAQs
1. What is the 7th Pay Commission (7th CPC)?
The 7th CPC revises pay, allowances, and pensions of central government employees, effective from January 1, 2016.
2. Who is eligible for 7th CPC pension revision?
All civilian pensioners who retired before 1st January 2016 are eligible.
3. How is the revised pension calculated under 7th CPC?
Pensioners can choose the higher of two methods:
Multiplying the 6th CPC pension by the fitment factor (2.57)
Calculating 50% of notional pay in the pay matrix
4. What is the fitment factor in 7th CPC pension calculation?
The fitment factor is 2.57, applied to the pension fixed under the 6th CPC to calculate interim pension.
5. What is notional pay in the pay matrix?
Notional pay is based on the last drawn pay, pay band, grade pay, and increments added before retirement.
6. How do I calculate 50% pension from notional pay?
After finding notional pay, divide it by 2 to get the revised pension amount.
7. Which method is more beneficial for pensioners?
Pensioners should choose the method that provides a higher pension. Often, Method 2 (pay matrix-based) gives higher benefits.
8. Are arrears paid under 7th CPC pension revision?
Yes, pensioners receive arrears when their final revised pension is implemented after the interim pension.
9. What is the role of the pay matrix in pension calculation?
The pay matrix standardizes pay levels, simplifies calculations, ensures transparency, and maintains parity between past and current retirees.
10. When was the 7th Pay Commission implemented?
The 7th CPC came into effect from 1st January 2016.